One of the most asked question in any Snowflake Data Engineer Interview is to explain the Snowflake architecture in detail. This concept is discussed in this article. It will help you in your upcoming interview.
Snowflake is a fully managed, cloud-native data platform designed for high performance, scalability, and simplicity. Its architecture separates storage, compute, and services, allowing each to scale independently for better cost management and flexibility.
1. The Three Core Layers of Snowflake Architecture
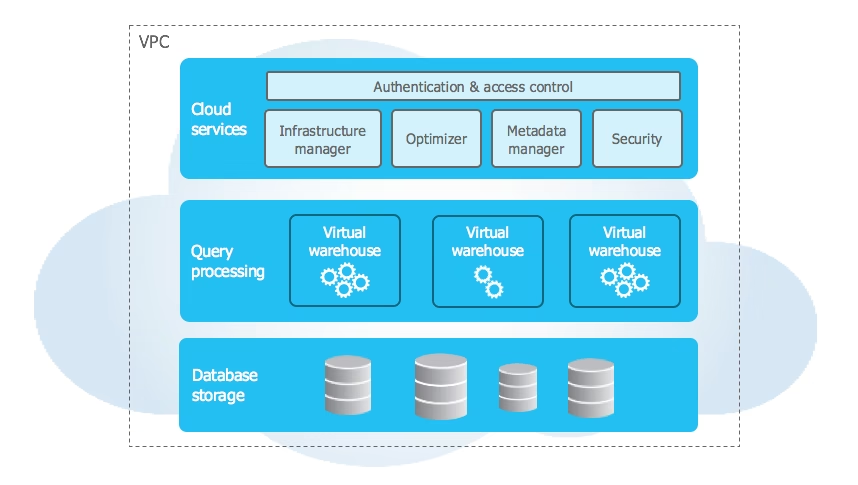
a) Database Storage Layer – The Data Foundation
Snowflake stores all table data and query results in a compressed, columnar format, organized into micro-partitions.
- Columnar Storage: Improves analytics by scanning only required columns.
- Micro-Partitions: Small, optimized storage units for fast access and high compression.
- Automated Management: Handles file size, compression, metadata, and optimization without user intervention.
- Cluster Keys: Improve query speed for large tables by grouping related data.
- Secure Access: Data is never directly accessible; only via SQL queries.
b) Query Processing Layer – The Compute Muscle
This layer runs queries using Virtual Warehouses — dedicated MPP compute clusters.
- Virtual Warehouses: Independent clusters (EC2 on AWS, VMs on Azure/GCP) that run queries.
- Elastic Scaling: Increase or decrease compute power instantly without downtime.
- Workload Isolation: Multiple warehouses can operate without impacting each other.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for compute time; auto-suspend/resume prevents waste.
- Parallel Execution: Enables high concurrency and faster results.
c) Cloud Services Layer – The Brain of the System
Coordinates all operations between compute and storage.
- Authentication & Access Control: Manages secure logins and roles.
- Metadata Management: Stores schemas, statistics, and execution plans.
- Security & Compliance: Enforces encryption, auditing, and governance.
- Serverless Operations: Automates tasks like Snowpipe (continuous ingestion), scheduled jobs, and materialized view refresh.
- Infrastructure Orchestration: Provisions and scales resources seamlessly.
2. Connecting to Snowflake
- Web UI: Browser based access for management and queries.
- SnowSQL CLI: Command line client for scripting and automation.
- ODBC/JDBC Drivers: Connect BI tools like Tableau and Power BI.
- ETL Integrations: Native connectors for Informatica, Datastage, Talend, and more.
Snowflake’s layered design — Storage as the foundation, Compute as the muscle, and Services as the brain — delivers powerful, flexible, and cost-effective data warehousing. It empowers businesses to focus on insights instead of infrastructure, while maintaining speed, scalability, and security.
Also Read NAB Data Engineer Walk-in Drive :
NAB Data Engineer Walk-In Drive: Shortest Flight Routes SQL Logic Challenge in Codility






Pingback: Understanding Micro-Partitions: Snowflake's Key to Scalable Performance
Pingback: American Express SQL Interview Questions - Tank Seekers
Pingback: Oracle’s Market Surge Highlights the Growing Influence of AI Trades - Tank Seekers
Pingback: ETL Developer Interview Questions:Gemini Solutions - Tank Seekers
Pingback: ETL Informatica Cloud Secure Agent - Tank Seekers